News and Articles
Related Product





Share Article
Are Thinner Thermal Pads Have Better Heat Transfer Capability?
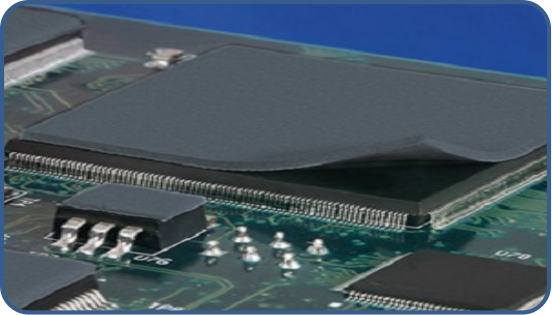
In general, thinner thermal pads will have better thermal conductivity than thicker ones.
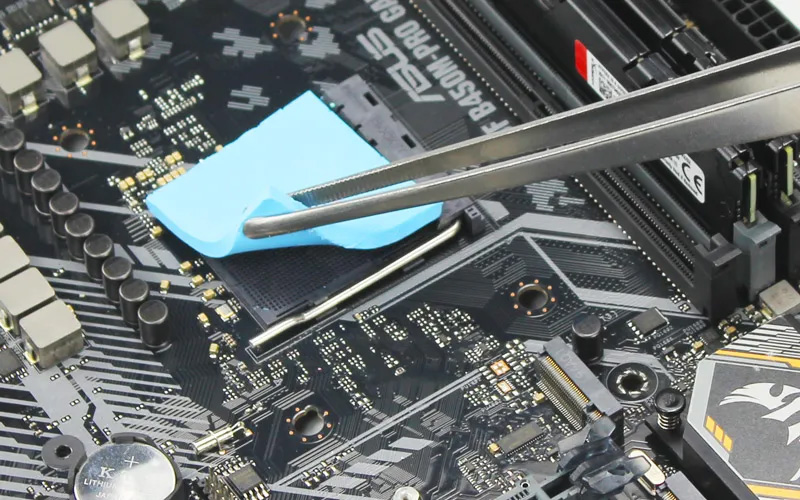
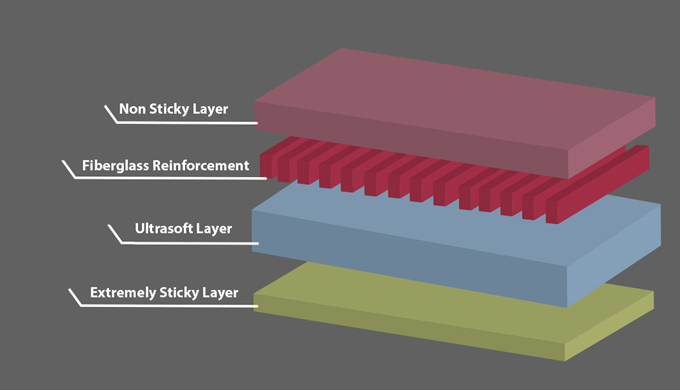
However, there are some exceptions to this rule. For example, if the thinner pad is made of a lower-conductivity material, it may not perform as well as the thicker pad. Thin thermal pads may not necessarily be better than thicker ones. The optimal thickness of a thermal pad depends on the specific application and the mating surfaces of the electronic components.
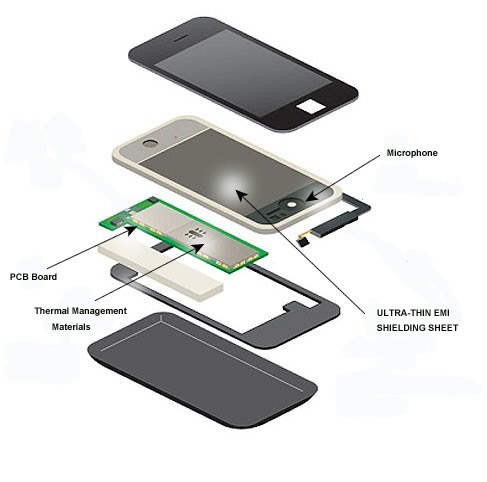
In general, thinner thermal pads are better for applications where the mating surfaces are very flat and smooth, as they allow the components to have better contact with each other. However, thicker thermal pads may be necessary for applications where there are larger gaps between the mating surfaces, or where there is a need for greater heat conductivity.
It's important to choose the appropriate thickness of thermal pad that will provide the best thermal transfer in your particular application, rather than assuming that thinner is always better.
Additionally, the thinner pad may not make good contact with the surface it is supposed to be cooling, which would also negatively impact performance.
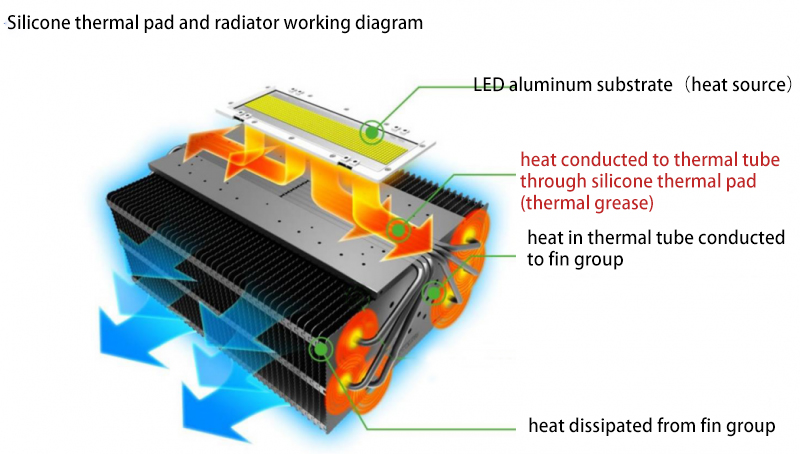
If the pad is too thin and does not make good contact with the surface of the heat sink, then you may need to use a thicker pad.
Thus, it is important to consider both thermal conductivity and contact area when choosing a thermal pad for your application. In most cases, a thinner thermal pad will be the better choice.